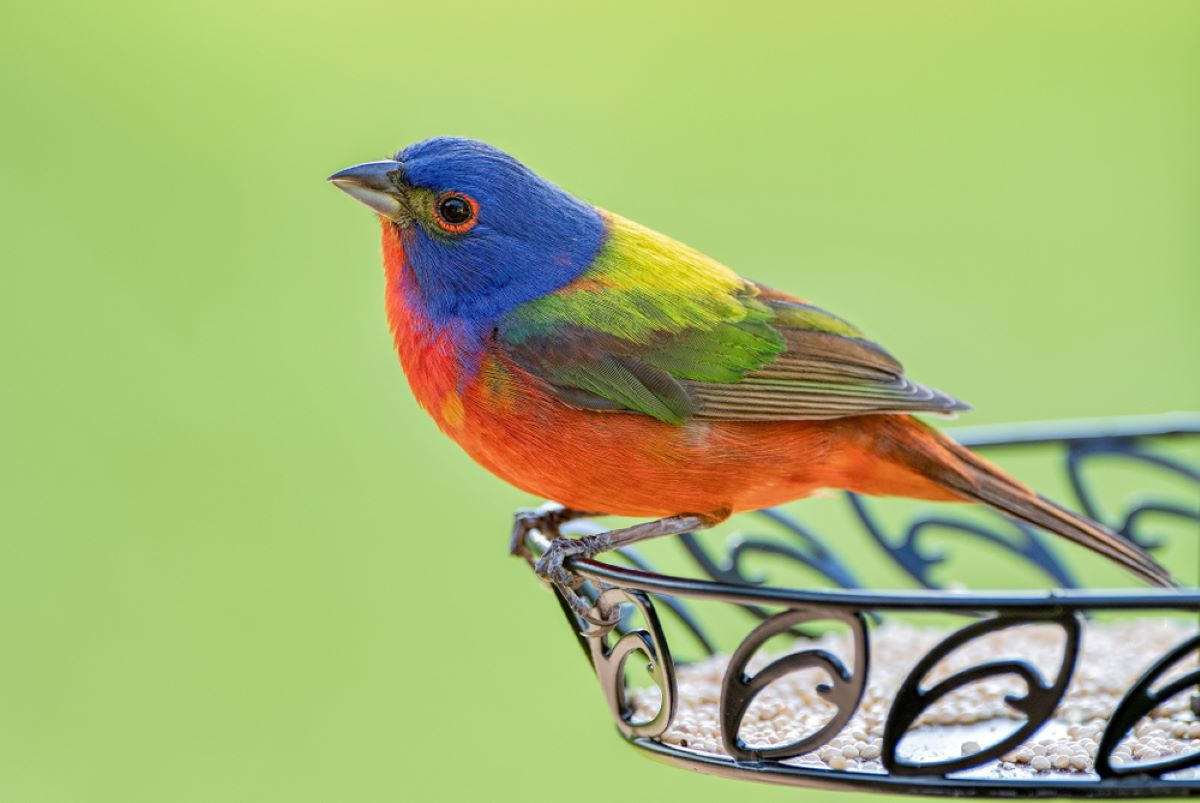
Painted bunting is one of the most colorful North American birds. Adult males are decorated with yellow, red, blue, and lime-green feathers. Adult females are fully bright green. Painted bunting population numbers are collapsing because of illegal capture, window collision, and cowbird parasitism.
Overall, the painted bunting is a magnificent bird known for its stunning colors, and observing one in the wild is a real treat for birdwatchers and nature enthusiasts.
As with all bird species, it’s essential to respect their habitats and observe them from a distance to avoid causing any disturbance.
How Common Are Painted Buntings?
The population of painted buntings is considered to be in decline, and they are not as common as some other bird species.
They’re frequent victims of window collisions and cowbird nest parasitism. Therefore, their numbers are dropping.
Additionally, they’re often caught and sold as cage birds (in Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean, and sometimes in Florida). This practice negatively affects their breeding populations.
As a result of these factors, painted buntings are classified as a species of conservation concern. While they are not listed as globally endangered, they may be considered threatened or of special concern in certain areas within their range.
What Does a Painted Bunting Look Like?
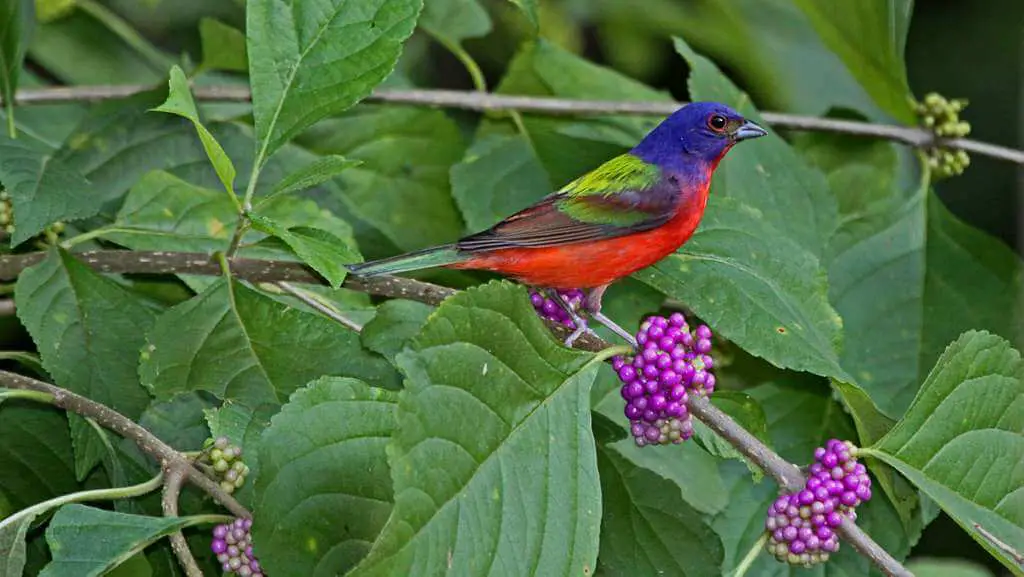
Painted buntings (Passerina ciris) are medium-sized songbirds with thick, seed-eating beaks. They are often described as “painted” due to the vibrant hues displayed on their plumage.
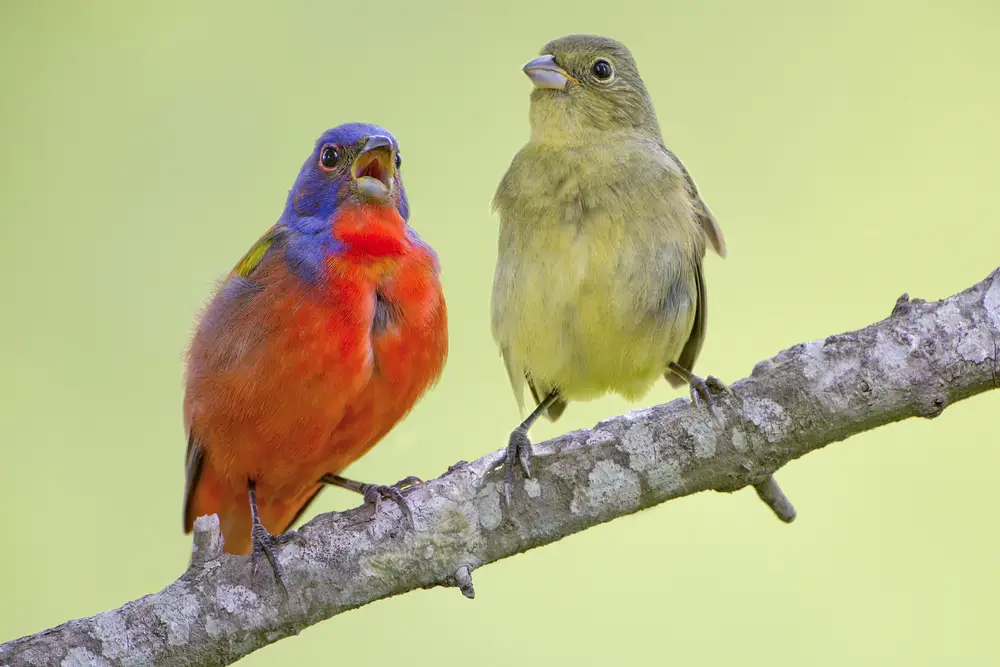
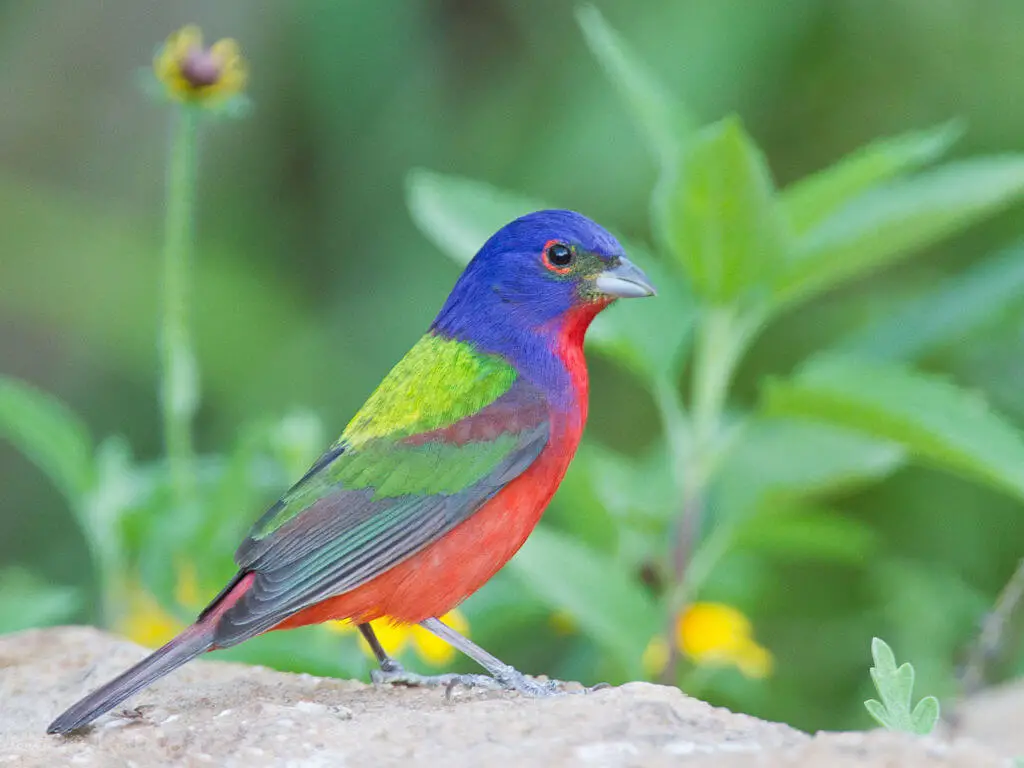
Adult male painted buntings are known for their vibrant plumage, while females and juveniles have a more subdued appearance.
Adult males are beautiful birds, with blue heads, reddish underparts, and lime-green backs. Luckily, you’ll hardly mix them with other species.
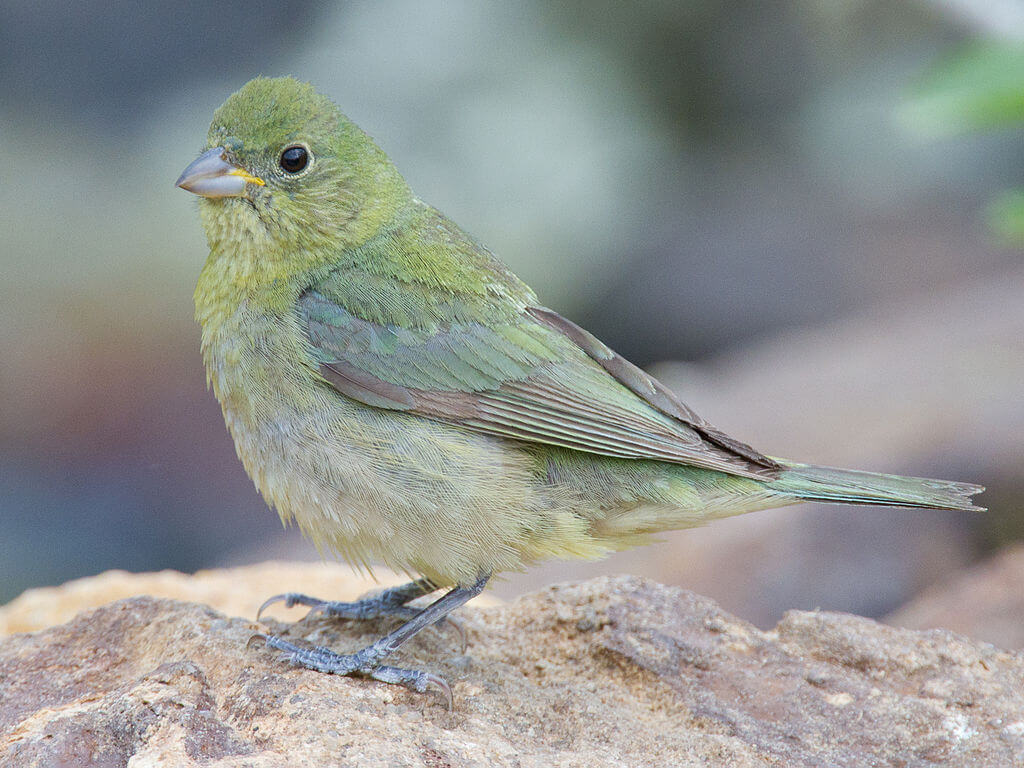
Adult females and immature males have a more understated appearance compared to the males. They are primarily green in color with a slight blue tinge on the wings and tail. The underparts are paler green or yellowish.



What is the habitat of Painted Buntings?
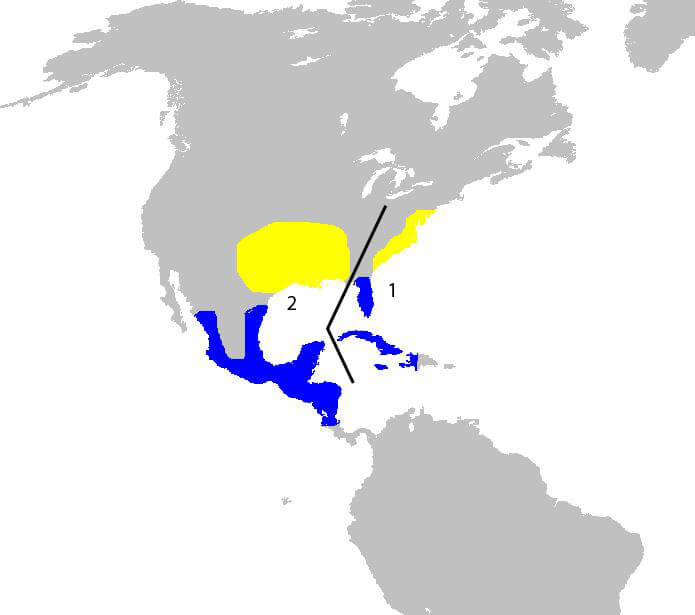
They are primarily a species of the southeastern United States during their breeding season and migrate to southern Mexico and Central America for the winter.
There are two subspecies of painted buntings:
- Passerina ciris ciris
- This is the nominate subspecies and is found in the southeastern United States, from Florida to the eastern parts of Texas.
- It is the most well-known and widespread subspecies of the painted bunting.
- Passerina ciris pallidior
- The pallidior subspecies breeds in the south-central United States and northern Mexico.
- Its range overlaps with the nominate subspecies but is generally found more to the west of the nominate subspecies’ breeding range.
Painted buntings will winter in Cuba, the Bahamas, Costa Rica, and western Panama. During the breeding season, they’ll distribute across two regions and cover the following places:
- New Mexico
- Southern Arizona
- Southern and Eastern Texas
- Oklahoma
- Louisiana
- Florida
- coastal Georgia
- and parts of South Carolina, North Carolina, and northern Mexico.
Throughout their range, painted buntings generally prefer areas with dense vegetation, providing them with ample cover and opportunities to forage for seeds and insects, which make up their diet.
They are known for their elusive and secretive behavior, often staying hidden within the thick foliage, which can make them challenging to spot despite their vibrant colors.
What Does a Painted Bunting Eat?
Painted buntings will forage food on the ground covered in grass. They’ll also eat from seed feeders. During migration, they’ll loosely bond with other seed-eating birds, such as indigo buntings.
Their favorite foods include:
- seeds
- insects (caterpillars, grasshoppers, flies)
- Occasionally, berries and fruits
So what are the best things to feed Painted Buntings?
- Sunflower Seeds: Black-oil sunflower seeds are highly preferred by painted buntings and many other bird species. They are a rich source of energy and nutrition.
- White Proso Millet: Millet is another favorite among painted buntings. White proso millet can be offered in bird feeders or scattered on the ground.
- Safflower Seeds: Safflower seeds are enjoyed by painted buntings and are also less attractive to squirrels and other nuisance birds, making them a good option for feeders.
- Nyjer (Thistle) Seeds: While Nyjer seeds are more commonly preferred by finches, painted buntings may also consume them if available.
- Cracked Corn: Adding some cracked corn to your bird feeders can be a good supplement to the diet, as it provides additional carbohydrates.
- Insects (during breeding season): During the breeding season, painted buntings incorporate insects into their diet to provide protein for themselves and their chicks. While it is challenging to offer live insects, you can provide suet cakes that may contain insects as part of the ingredients.

What About Nesting and Eggs?
The female is responsible for building the nest. The nest is a cup-shaped structure made of grasses, leaves, stems, and other plant materials. The female weaves the materials together to create a sturdy and well-insulated nest.
The nests are typically placed in low shrubs, thickets, or small trees, usually at a height of 1 to 5 feet (about 30 to 150 centimeters) above the ground.
Painted bunting clutches usually consist of 3 to 4 eggs, although they can occasionally have more. The eggs are small and usually pale blue or greenish-blue in color with speckles or spots. The coloring of the eggs can help camouflage them within the nest.
The female incubates the eggs for about 11 to 14 days. During this time, she stays on the nest to keep the eggs warm and protected.
After the eggs hatch, both the male and female take turns feeding the chicks and keeping them warm. The chicks fledge, or leave the nest, about 10 to 14 days after hatching.
What Does Painted Bunting Sound Like?
The painted bunting has a distinctive and melodious song that is quite unique. The male’s song is a series of musical and high-pitched notes that are often described as sweet and cheerful.
Female painted buntings have a simpler and softer call that is more of a soft, chattering note than a full song.
Indiahoma, Comanche County, Oklahoma
Make sure to also check our article on What Do Indigo Buntings Sound Like?
What are some of the ways Painted Bunting can be helpful to humans?
Painted buntings primarily play a role in the ecosystem as part of the natural food web and help with seed dispersal.
While they may not have direct benefits to humans in the same way that some other species do, their presence in the environment is valuable for maintaining biodiversity and promoting healthy ecosystems.
How Do I Attract Painted Buntings to My Yard?
Keep in mind that these birds have specific habitat preferences and can be quite shy, so creating an inviting environment requires some effort.
Here are some tips to attract painted buntings to your yard:
- Provide Suitable Habitat: Plant native shrubs, bushes, and small trees to create a thicket-like environment. Consider species like wax myrtle, yaupon holly, viburnum, and American beautyberry, which offer both cover and potential food sources.
- Offer Proper Food: Painted Buntings are primarily seed-eaters. Set up bird feeders with a mix of seeds such as sunflower seeds, millet, safflower seeds, and nyjer (thistle) seeds. Adding white millet to your feeders can be especially attractive to these colorful birds.
- Create a Water Source: Having a bird bath or a shallow water feature can be appealing to painted buntings, especially in warmer months when water for drinking and bathing is essential.
- Use Natural Colors: Painted buntings are attracted to vibrant colors. You can use colorful plants or even place some brightly colored objects, like garden ornaments or wind spinners, in your yard to catch their attention.
- Add Native Plants: Native plants attract a wide variety of insects, which can serve as a food source for painted buntings during the breeding season. Insects are an essential part of their diet, especially when raising chicks.
Remember that they are migratory birds and may visit your yard during their breeding season or migration period.
Be patient and create a welcoming environment, and you may have the opportunity to enjoy the beauty of these colorful birds in your own backyard.
What to read next: Indigo Bunting Identification, Habitat And Lifespan

